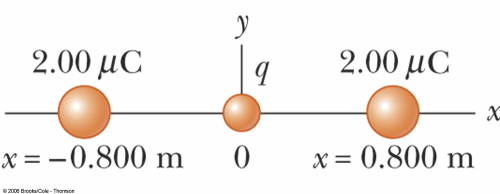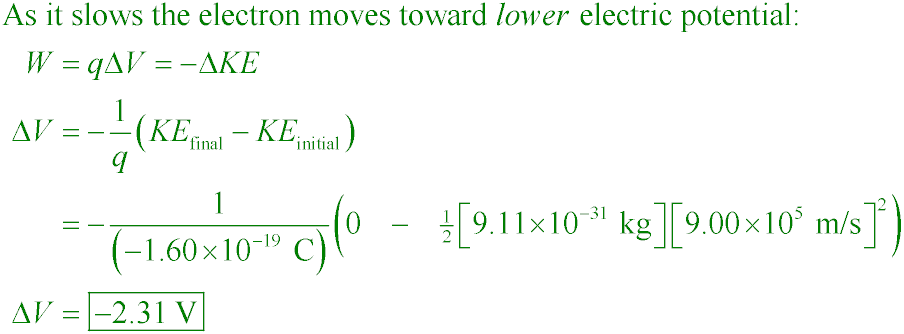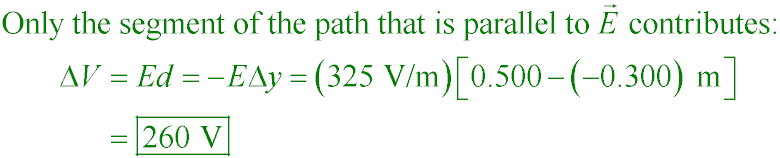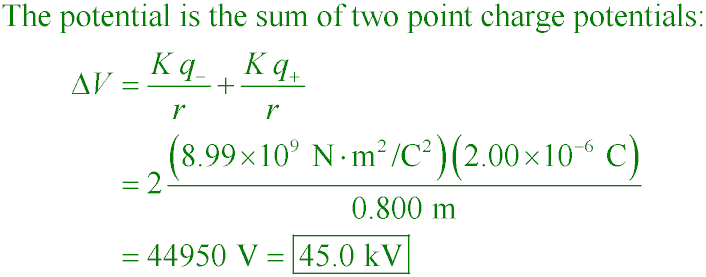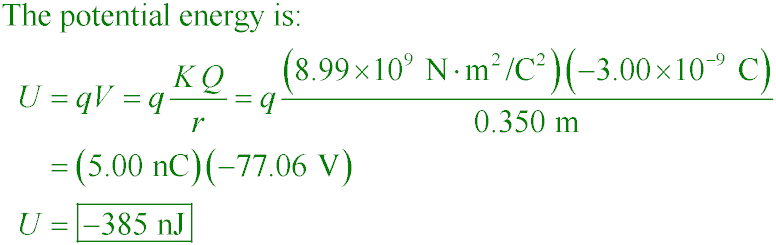Summary
- Electric flux
- Gauss's law
- Fields and conductors
POP5 QQ19.6
If the net flux through a gaussian surface is zero, the following four statements could be true.
Which of them must be true?
A. The number of electric field lines entering the surface equals the number leaving the surface.
B. The electric field is zero everywhere on the surface.
C. The net charge inside the surface is zero.
D. There are no charges inside the surface.
E. A and C must be true.
F. B and D must be true.
G. All must be true.
H. None must be true.
Answer
POP5 20.03
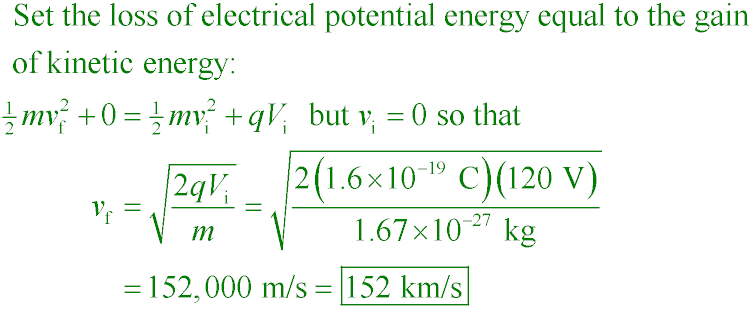
Calculate the speed of a proton accelerated from rest through 120 V.
A. 23.1 Gm/s
B. 6.49 Mm/s
C. 152 km/s
D. 120 m/s
Answer
PSE6 25.04
What potential difference is needed to stop an electron having an initial speed of
9.0×105 m/s?
A. −0.502 V
B. −1.25 V
C. −0.028 V
D. −2.31 V
Answer
POP5 20.01
Consider the points A = (−0.200, −0.300) m and B = (0.400, 0.500) m. Find
the potential difference VB − VA for the configuration of
Fig. P25.9 using the blue path if E = 325 V/m.
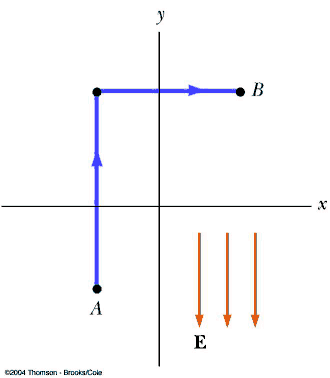
A. 455 V
B. 260 V
C. 325 V
D. −325 V
Answer
POP5 20.09c
What is the electric potential at the origin for the charge configuration shown below?
A. 400 V
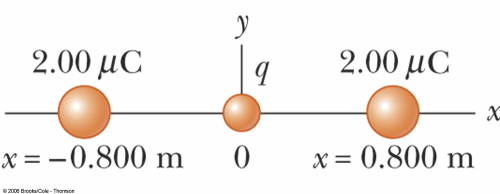
B. 800 V
C. 22.5 kV
D. 45.0 kV
Answer
PSE6 25.20
Two point charges of +5.00 nC and −3.00 nC are separated by 35.0 cm. What is the potential energy
of the pair?
A. +385 nJ
B. −385 nJ
C. +1.10 µJ
D. −1.10 µJ
Answer
Walker5e EYU 20.1
The electric potential in system A changes uniformly by 1000 V over a distance of 10 m; in system B the
electric potential changes uniformly by 1 V over a distance of 1 cm. The magnitude of the electric field in
system A is _____ the magnitude of the electric field in system B.
A. greater than
B. less than
C. equal to
Answer
E. A and C must be true.
Only those two statements are always consistent with Gauss's law
in this situation.
C. 152 km/s
D. −2.31 V
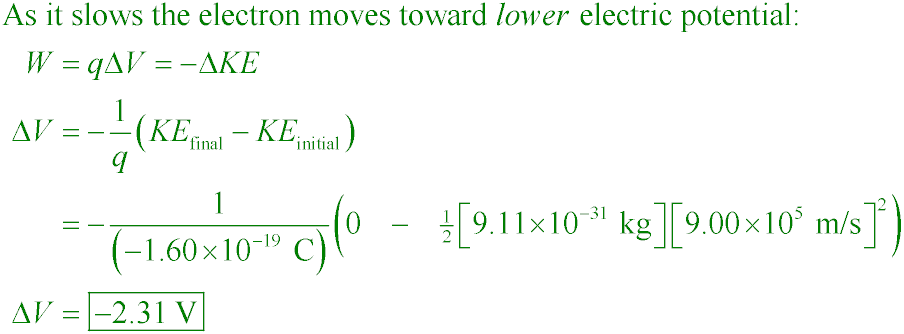
B. 260 V
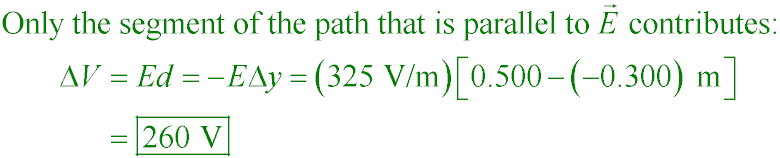
D. 45.0 kV
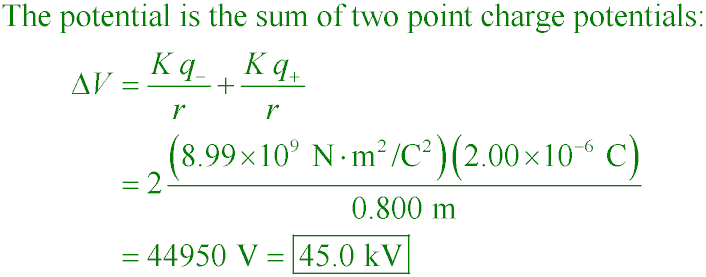
B. −385 nJ
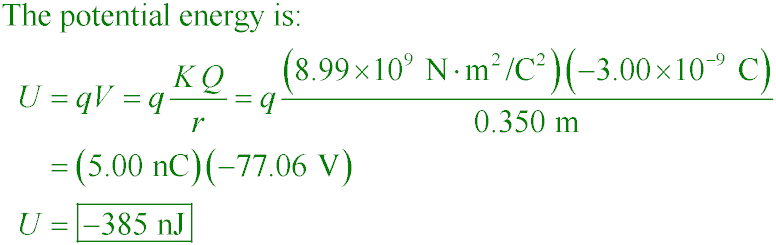
The negative sign is due to the attractive force. The charges
are now in a "potential well" and it will take 385 nJ of work to pull the charges apart until they
are infinitely separated.
C. equal to
The magnitude of the electric field is the ratio of the change in potential
ΔV to the displacement Δs. In this case, 1000 V divided by 10 m yields an electric
field of 100 V/m (or 100 N/C), the same as 1.0 V divided by 0.010 m.
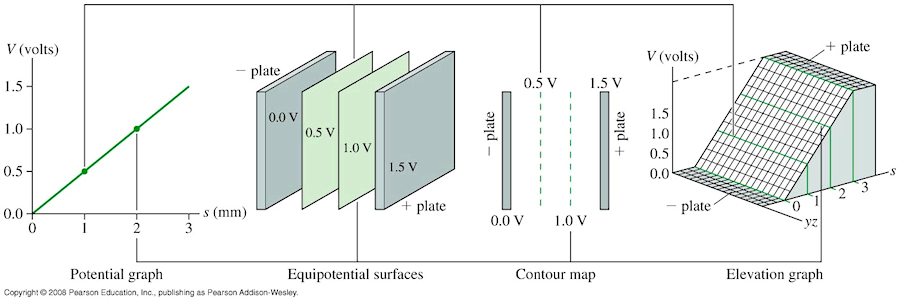
Another way to think about it is to remember voltage is like elevation and field is like slope. Although 1000 V
represents an elevation change 1000 times bigger than 1.0 V, 10 m is 1000 times farther than 1 cm. Hence the slope
of the "terrain" is the same; it increases by 100 V each meter of displacement.