Summary
- Thomson model
- Rutherford model
- Bohr model
- de Broglie waves
Chapter 5
- de Broglie and Bohr, interactive animation
Example #1
- de Broglie and Bohr video 8:22 - 12:32

- Matter waves
- QM hydrogen atom
- electron corrals
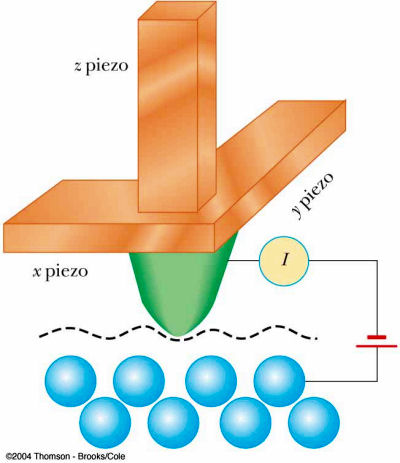
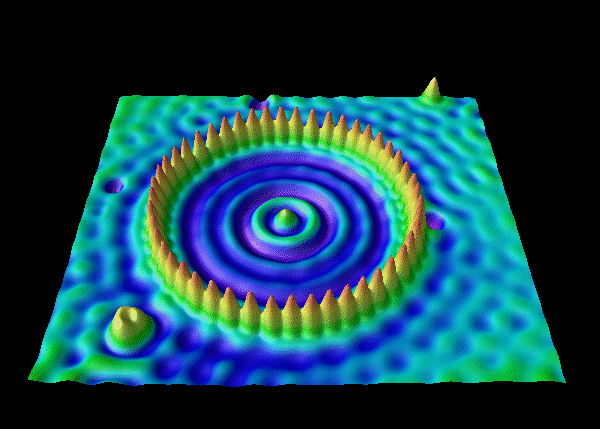
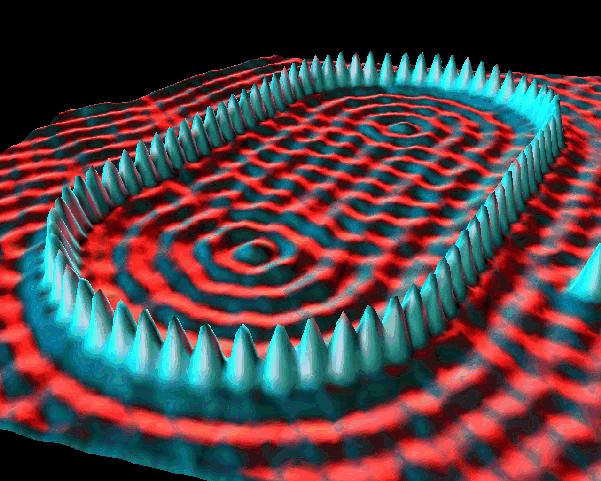

- de Broglie waves continued
- Example problem 5.6
- Example problem 5.12
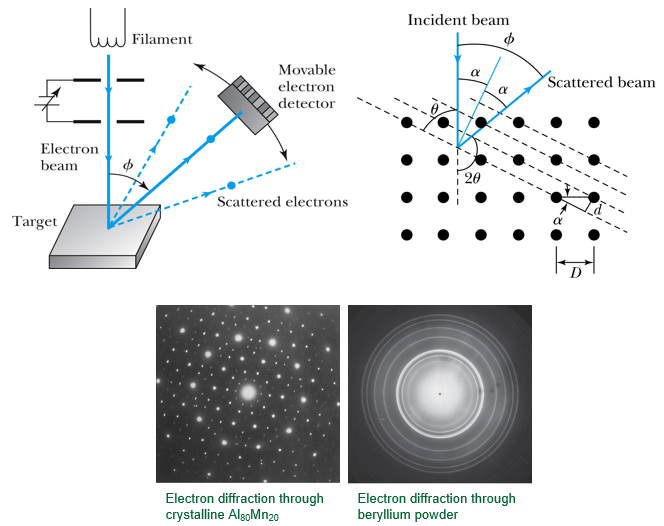
- Bragg's law X ray diffraction 2d sin θ = n λ
- Davisson-Germer electron diffraction D sin ϕ = n λ
- Example problem 5.3
- The QM free particle applet
- wave packets and Fourier analysis applet
- Schrödinger's wave theory video 12:20 - 14:46
- group and phase velocities
- dispersion applet
- Example problem 5.24
- Example problem 5.28
Walker5e EYU 31.4
What is the principal quantum number n for the Bohr orbit depicted below?
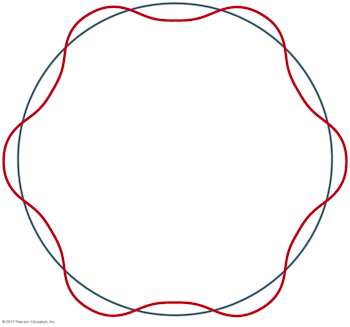 A. 1
A. 1
B. 5
C. 6
D. 10
E. 12
Answer

C. 6
A careful accounting of the complete wavelengths that span the circumference of the orbit reveals there are six, which corresponds to the value of the principal quantum number.






 A. 1
A. 1