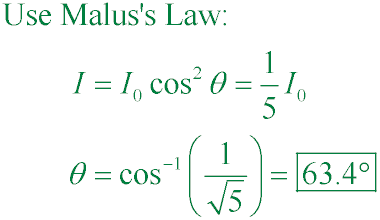Summary
- Single-slit diffraction
- Circular apertures
- Diffraction gratings
Today's joke
Quiz bonus Ch.37
Material NOT on Final Exam
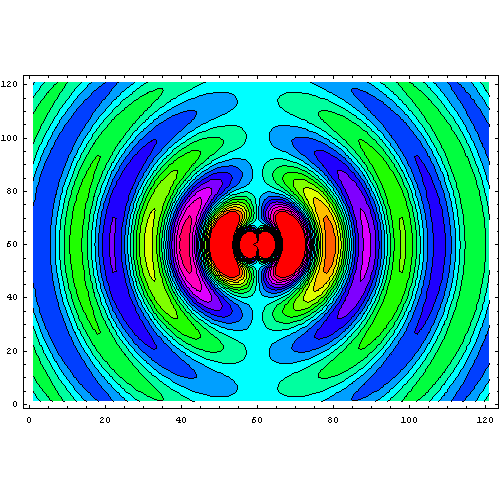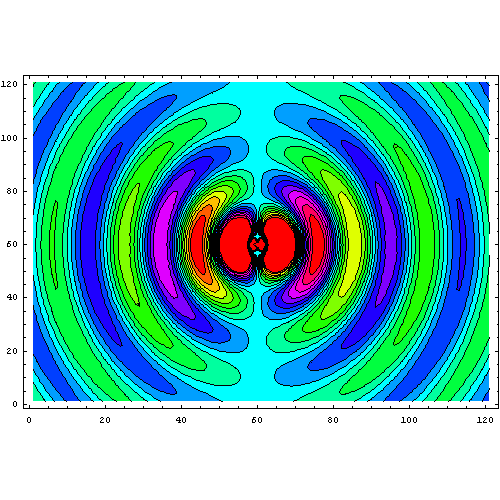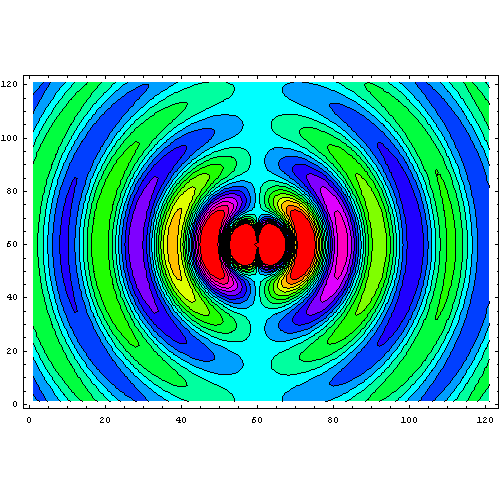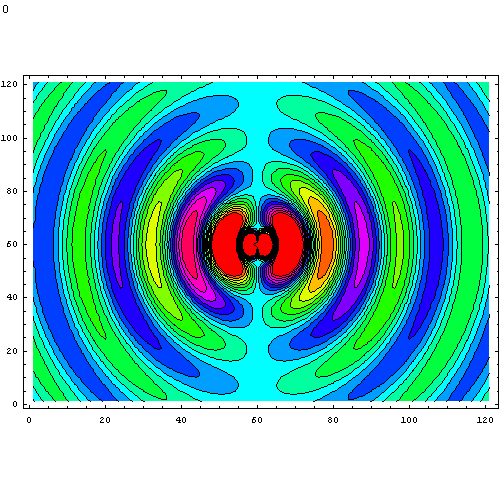
This animation of dipole radiation is from Wikipedia.
You can also explore an
interactive applet
by Paul Falstadt. Chose "Oscillating dipole" from the Setup list. There is also a
3-D version
but it's a little more difficult to see what's going on. Choose "dipole source" from the Setup list.
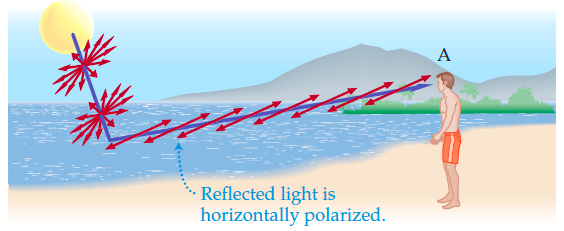
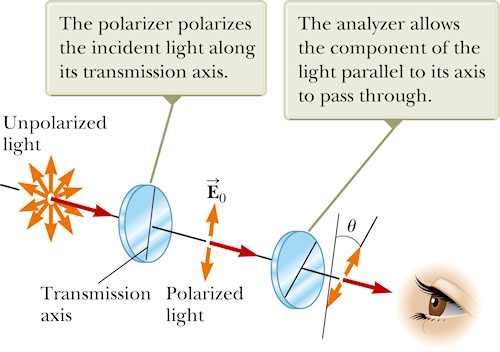
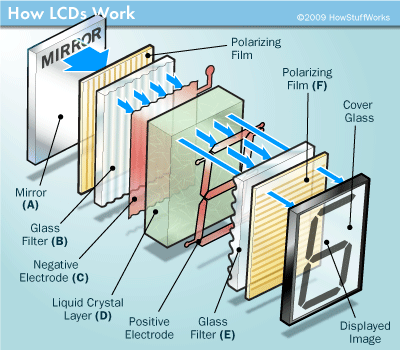
- Polarization of light
POP5 27.qq.5
Suppose you are observing a binary star with a telescope and are having difficulty resolving the
two stars. You decide to use a colored filter to maximize the resolution. A filter of a given
color transmits only that color of light. What color filter should you choose?
A. red
B. yellow
C. green
D. blue
Answer
POP5 24.45
A light beam of intensity I0 is polarized parallel to the transmission axis of a single polarizing filter. Through what angle θ should the polarizer be rotated to reduce the transmitted intensity I to I0/5?
A. 78.4°
B. 63.4°
C. 54.7°
D. 18.0°
Answer
POP5 24.qq.7
A polarizer for microwaves can be made as a grid of parallel metal wires about a centimeter apart. How is the
electric field vector oriented for microwaves transmitted through this polarizer?
A. parallel to the wires
B. perpendicular to the wires
C. 45° relative to the wires
D. circularly polarized
Answer
D. blue
The angular size of the Airy disk diffraction pattern formed by a
circular aperture is linearly proportional to the wavelength of light. Thus the shortest
wavelength visible light, blue, will produce the smallest Airy disk diameter and the best
resolution.
B. 63.4°
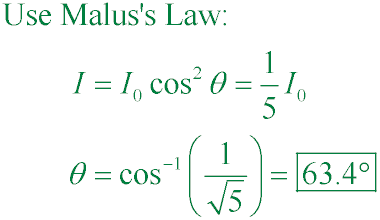
B. perpendicular to the wires
The electric field parallel to the wires will drive current in the wire,
which will dissipate energy as heat due to Ohmic resistance. Therefore, the electric field component
parallel to the wires will be extinguished, but the perpendicular component will pass through the grid.