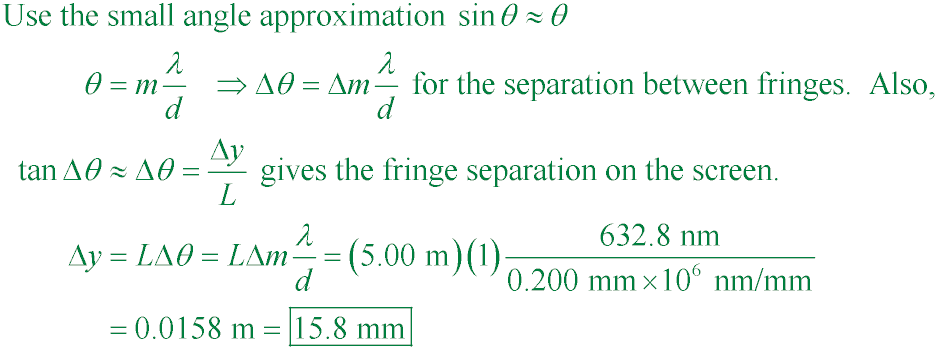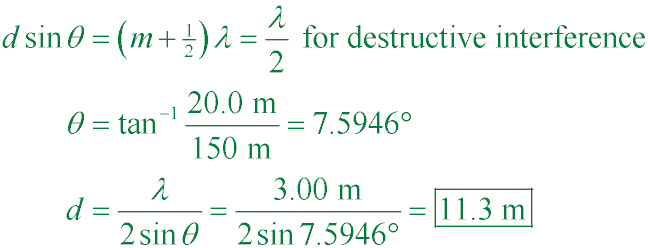Summary
- Refraction images
- Thin lenses
- Wave reflection and transmission
POP5 26.qq.6
If you cover the top half of the lens in the figure with a piece of paper, what happens to the appearance of
the image?
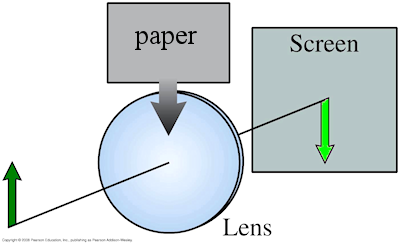
A. The bottom half disappears.
B. The top half disappears.
C. The entire image is visible but dimmer.
D. The entire image inverts upside-down.
Answer
PSE6 37.1
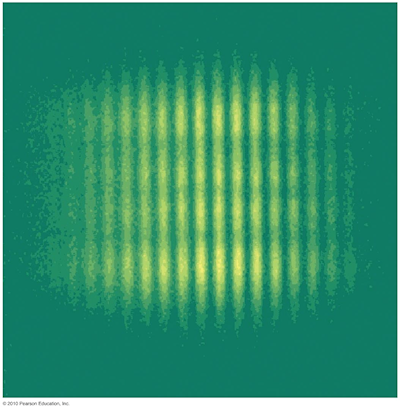
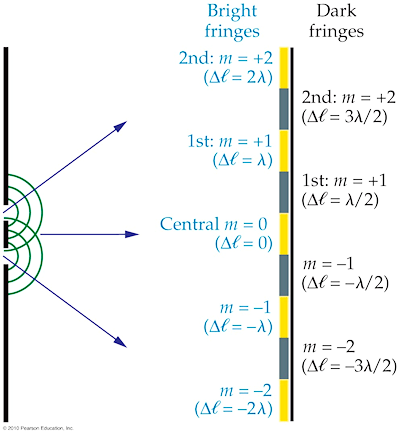
A λ = 632.8 nm laser beam strikes two slits that are 0.200 mm apart. How far
apart are the bright fringes on a screen 5.00 m away?
A. 3.16 mm
B. 25.3 mm
C. 4.57 mm
D. 15.8 mm
Answer
POP5 27.17
The walls of a riverside warehouse has two open doors and its walls are lined with sound-absorbing
material. Two people y = 20 m apart are L = 150 m from the doors. Person A can hear
λ = 3.00 m
sound waves from a boat horn loudly, but they are barely audible to person B. Assuming that person B
is at the position of the first minimum,
determine the distance d between the doors, center to center.
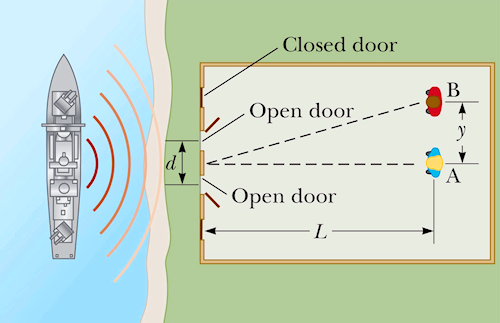
A. 11.3 m
B. 8.81 m
C. 7.50 m
D. 5.33 m
Answer
kw4
Why don't we notice interference patterns when we turn on two lights in a room?
A. The lights aren't in phase.
B. The lights are too bright.
C. The lights are too dim.
D. The air molecules disturb the interference pattern.
Answer
Walker5e 28.EYU.2 mod
If the frequency of light in a two-slit experiment is increased, the angle to the first bright fringe above the central bright fringe will_____.
A. increase
B. decrease
C. stay the same
Answer
Walker5e 28.11
Moe, Larry, and Curly stand in a line with a spacing of 1.00 m. Larry is 3.00 m in front of a pair of stereo speakers 0.800 m apart. If the speakers vibrate in phase, what are the two lowest frequencies that allow Larry to hear a loud tone while Moe and Curly hear very little? The speed of sound is 343 m/s.
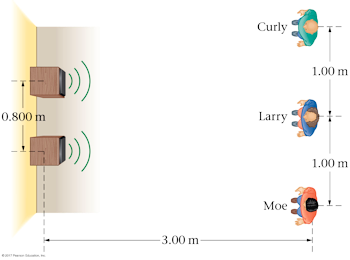
A. 226 Hz and 678 Hz
B. 339 Hz and 1017 Hz
C. 1085 Hz and 2170 Hz
D. 678 Hz and 2034 Hz
Answer
C. The entire image is visible but dimmer.
The paper blocks half of the light rays, and the image becomes dimmer.
However, the other half of the lens still directs rays to every part of the real image of the candle, so
the entire image is visible. This is an example of an aperture stop, which limits the total amount
of light that passes through a system (like the aperture setting of a camera). A field stop at the
film plane (the location of the real image) would indeed block half of the image.
Ray diagram with the lens unblocked:
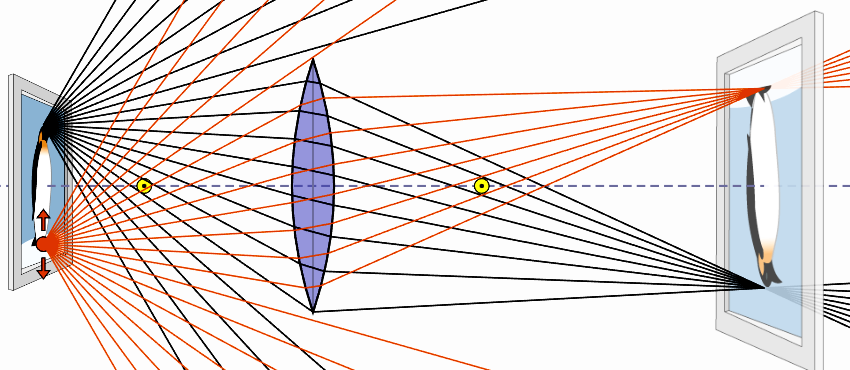
Ray diagram with the lens half blocked:
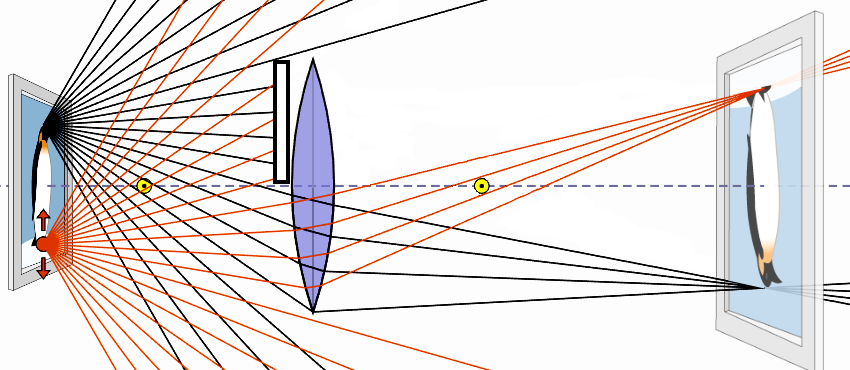
D. 15.8 mm
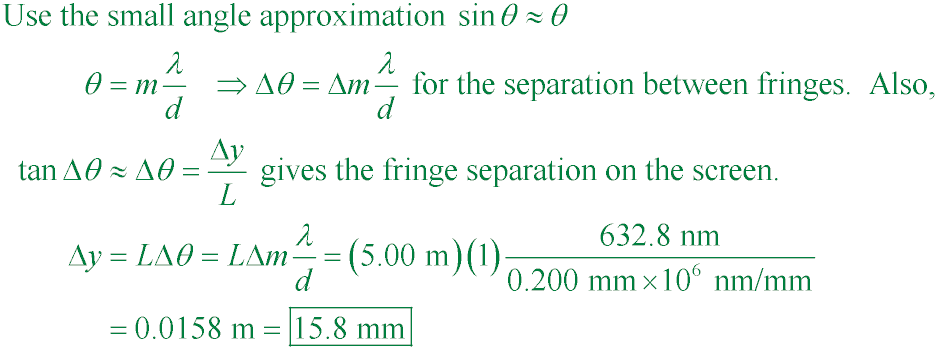
A. 11.3 m
A. The lights aren't in phase.
In order to see constructive and destructive interference, there must be a fixed phase relationship between the waves coming from various sources. There is no such relationship for light waves emitted from two different light bulbs. The light bulbs also emit many different wavelengths simultaneously, further complicating efforts to detect wave interference.
B. decrease
A higher frequency corresponds to a shorter wavelength. Waves of shorter wavelength spread out (diffract) less after passing through the slits, and the short wavelength leads to a smaller angle at which constructive interference (one wavelength path difference between the two waves) will occur. You can also see the angle decreases when the wavelength decreases by examining the formula, d sin(θbright) = mλ.
D. 678 Hz and 2034 Hz
We need to find the two lowest frequencies that produce destructive interference at the positions of Moe and Curly. Larry will always hear a loud sound (constructive interference) at his location no matter the frequency.