Example #1
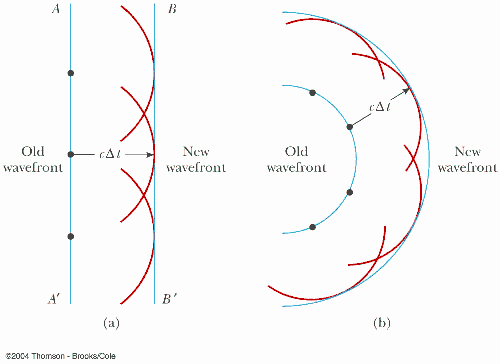
- Diagram
- reflection & refraction
- total internal reflection
- Animated applet
Example #2
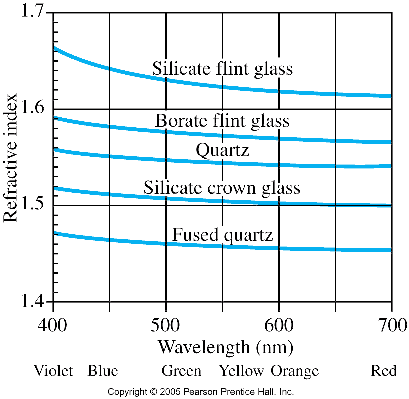
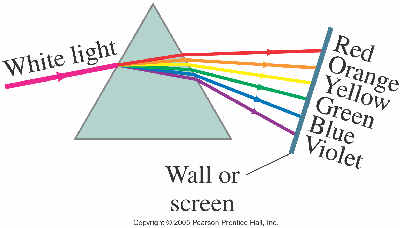


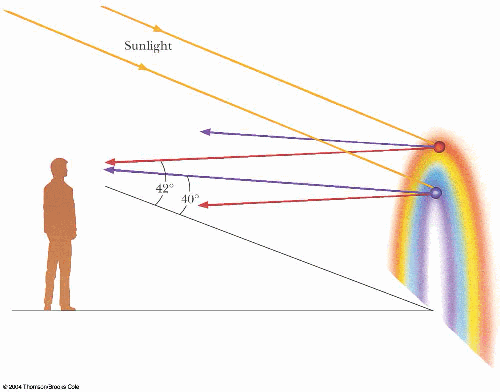
_2014-10-10.png)
Try this additional example
Read textbook sections 34-1 and 34-2 before the next lecture
 [supplemental material]
[supplemental material]
|
Green flash only rarely seen at sunset is caused by a
competition between dispersive refraction and scattering
in the atmosphere.
This photograph was taken from Torrey Pines, California on Jan. 7, 1996, by Andrew T. Young. |

|
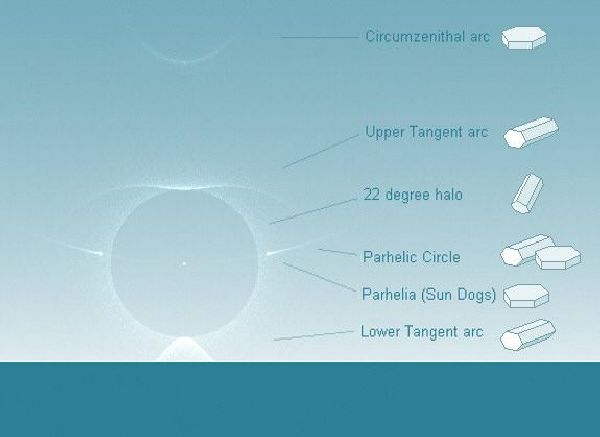
More photos of halos
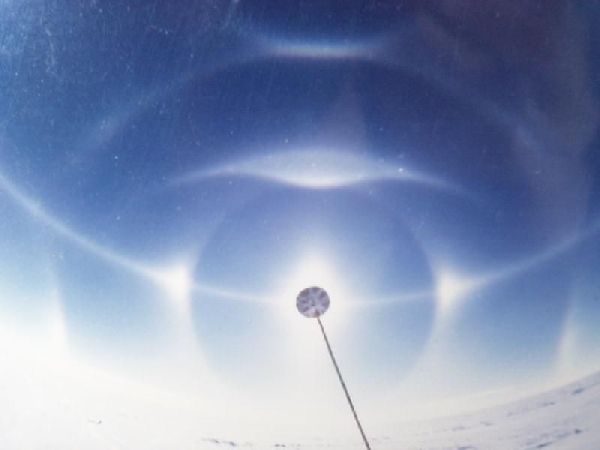

This picture was taken at the south pole, and includes a great number of interesting optical effects created by pencil-shaped and plate-shaped ice crystals.
These are the ice crystals responsible for some of the effects you see in the above photo
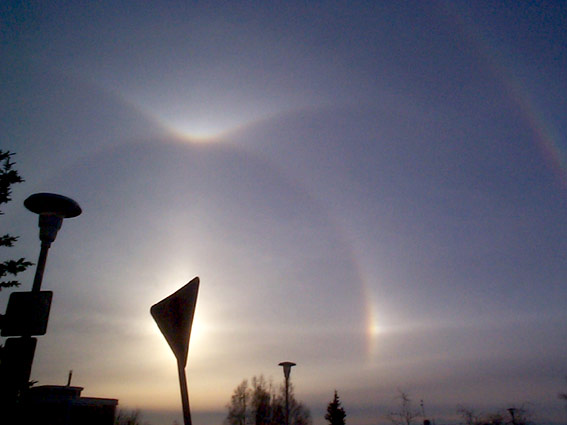

This picture was taken in Alaska, and shows some color in the sun dogs and other effects that result from slight dispersion in ice.