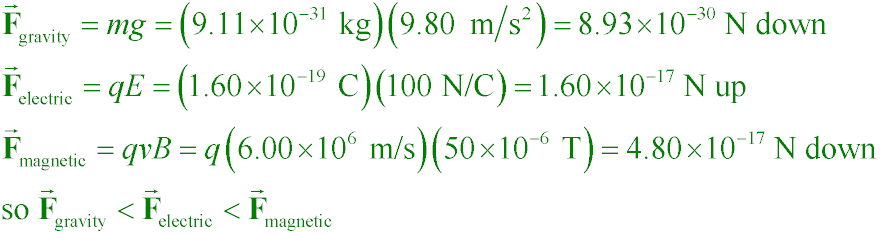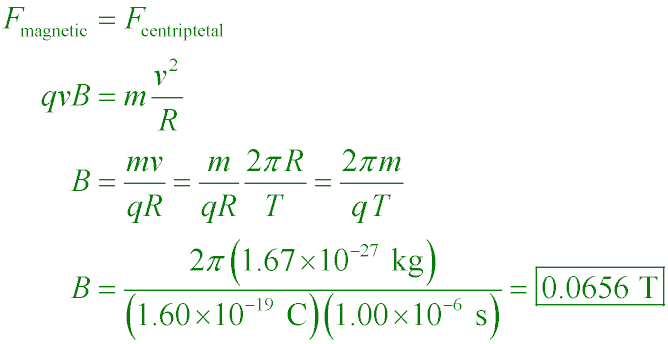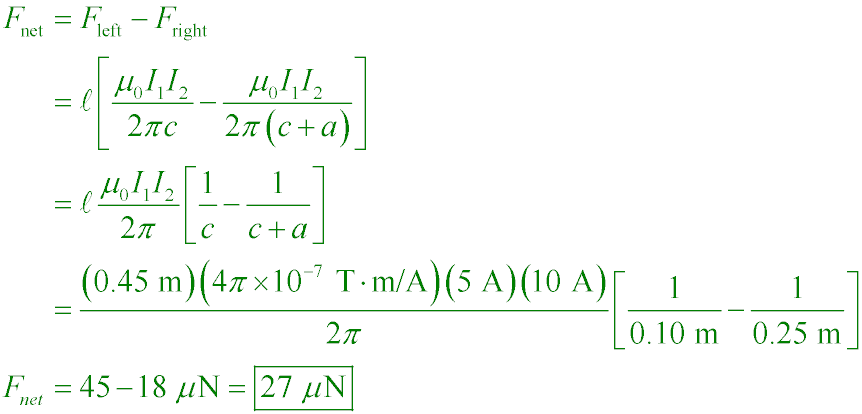Summary
- RC circuits
- Magnetism
- Vector cross products
klm
In the circuit segment shown, if
C = 5.0 µF,
Q = 15 µC,
ℰ = 6.0 V,
R = 4.0 Ω, and
I = 3.0 A,
what is the potential difference Vb − Va?

A. +21.0 V
B. +9.00 V
C. +6.00 V
D. −3.00 V
Answer
POP5 22.6
If B = 50 µT northward and E = 100 N/C downward, how do the magnitudes
of the forces on an electron compare if it has a velocity of 6000 km/s eastward?
A. gravity < electric < magnetic
B. electric < gravity < magnetic
C. electric < magnetic < gravity
D. magnetic < electric < gravity
Answer
PSE6 29.32
A proton moving in a circular path has a period of 1.00 µs. What is |B|?
A. 1.00 µT
B. 55.2 µT
C. 33.3 mT
D. 65.6 mT
Answer
POP5 22.43
What is the net force exerted on the loop if I1 = 5.00 A, I2 = 10.0 A,
c = 0.100 m, a = 0.150 m, and l = 0.450 m?

A. 27.0 µN right
B. 27.0 µN left
C. 923 µN right
D. 923 µN left
Answer
PSE6 29.14
A conductor with mass/length = 0.0400 kg/m is suspended as shown in the figure. What current will produce
zero tension in the supporting wires if B = 3.60 T?

A. 57.3 mA
B. 109 mA
C. 525 mA
D. 1.77 A
Answer
POP4 q22.10
 Two perpendicular wires are almost touching and carrying currents in the manner shown. What is the
force between the wires?
Two perpendicular wires are almost touching and carrying currents in the manner shown. What is the
force between the wires?
A. strong and attractive
B. strong and repulsive
C. weak and attractive
D. zero
Answer
PSE6 29.22
Ten windings of wire are formed into a square of side length 0.100 m. The coil is hinged along a
horizontal side, carries a 3.40-A current, and is placed in a vertical magnetic field of
magnitude 0.0100 T. Determine the angle that the plane of the coil makes with the vertical when
the coil is in equilibrium.

A. 4.0°
B. 12°
C. 21°
D. 29°
Answer
Walker5e CnEx 22-12
When the switch is closed the wire between the poles of the horseshoe magnet deflects downward. Is the left end of the magnet a north magnetic pole or a south magnetic pole?
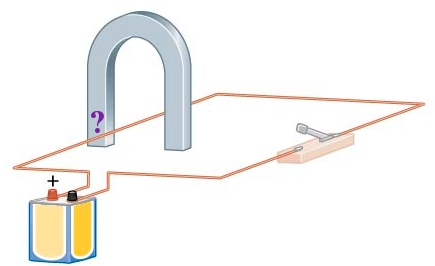
A. north
B. south
C. either pole produces a downward deflection
Answer
Walker5e 22.64
Four wires each carry current I in the directions shown. What is the direction of the magnetic force experienced by wire 2?

(Select the direction indicated by the letters)
Answer
A. gravity < electric < magnetic
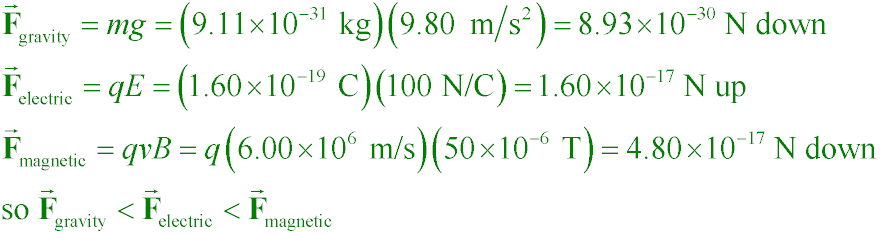
D. 65.6 mT
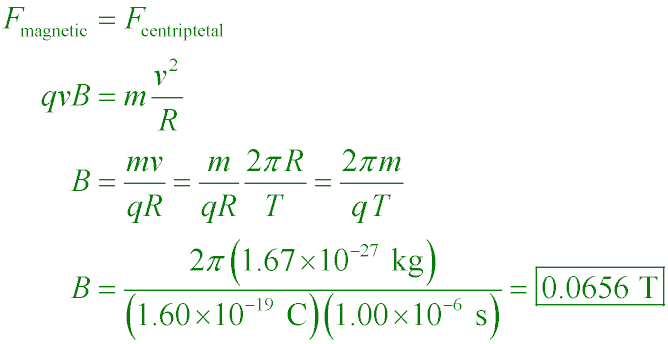
B. 27.0 µN left
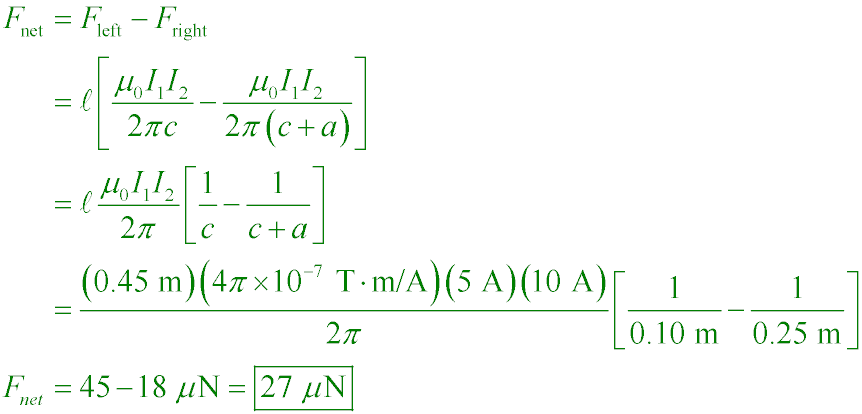
B. 109 mA

You can also
suspend a live frog
in a magnetic field! However, the physics of how this happens is a little different than
the force on an electric current.
D. zero
The magnetic field from one wire is everywhere parallel to
the current in the other wire. Therefore, the magnetic force per length
I × B is zero.

A. 4.0°


A. north
Using the right-hand-rule, if your thumb points downward (the direction of the force) your fingers curl toward the right (the direction of the magnetic field). Magnetic fields come out of the north pole and enter the south pole of a magnet.
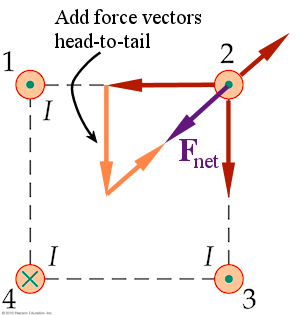
Direction f
Wire 2 will be attracted by wires 1 and 3 but repelled by wire 4. The repulsive force from wire 4 will be smaller than the other two forces because wire 4 is farther away. Adding the vectors head-to-tail reveals a net force toward wire 4, or in the direction indicated by "f".
The photo above depicts aurora loops around the southern
polar region in the distance as viewed by astronauts onboard the space shuttle Discovery on STS-39 in 1991.
Aurora are formed at the poles of the earth where charged particles
from the sun spiral around the magnetic fields of the earth and slam into the atmosphere, ionizing the
gas molecules and causing them to emit light.
Source: NASA Image Exchange

Red and green colors predominate in this view of the Aurora Australis
photographed from the Space Shuttle in May 1991 at the peak of a geomagnetic maximum.
Source: NASA Earth Observatory

Here is another photograph of the southern lights taken by astronauts onboard the Space Shuttle Discovery. The
emissions, extending nearly vertically upward, trace out the Earth's magnetic field lines. The green glow occurs
at altitudes near 80-120 kilometers. The red glow is less energetic and occurs at altitude above 250 kilometers.
Both types of light are produced by oxygen atoms in the atmosphere. Photos provided courtesy of NASA, Astronaut
Overmeyer and Dr. Hallinan. The source of this material is
Windows to the Universe
at the University Corporation for Atmospheric Research (UCAR). ©1995-1999, 2000
The Regents of the University of Michigan; ©2000-01 University Corporation for Atmospheric Research.
All Rights Reserved.

Here is an even better photo from the International Space Station (See a movie!)
Of course, auroras are also visible from earth!

Aurora photographed by Markus Varik on February 19, 2018 in Tromsø, Norway. From the
spaceweather.com
real-time aurora gallery

Aurora photographed by Mark Taylor on September 12, 2014 in central Maine. From
phys.org/news/2015-01-northern.html
- Blue: nitrogen 0 to 60 mi altitude
- Red: oxygen 150+ mi altitude
- Green: oxygen 60 to 150 mi altitude
- Yellow: mixture of red and green







 Two perpendicular wires are almost touching and carrying currents in the manner shown. What is the
force between the wires?
Two perpendicular wires are almost touching and carrying currents in the manner shown. What is the
force between the wires?