Summary
- Series and parallel circuits
- Kirchhoff's laws
- RC circuits
Chapter 28
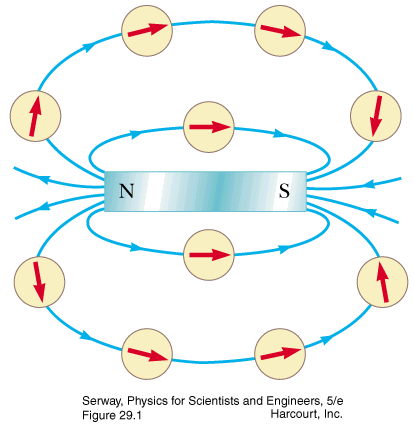

- Magnetism
- magnet properties
- magnetic field applet

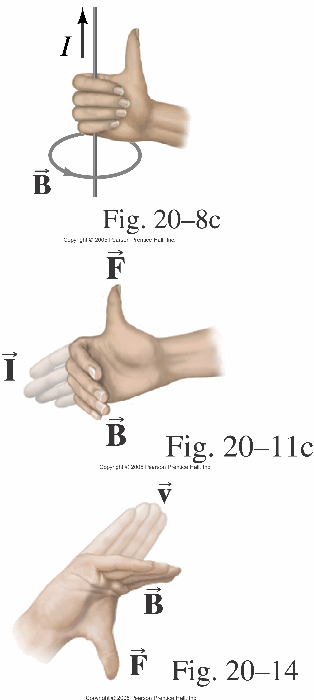
- The vector cross product
- properties
- The right-hand rule
- unit vectors
- torque applet
- Cross product as a determinant of a matrix
- Practice:
Try these additional examples
Example #2
Example #3
- Prepare:
Read textbook sections 28-2 through 28-5 before the next lecture
POP4 22.Q14
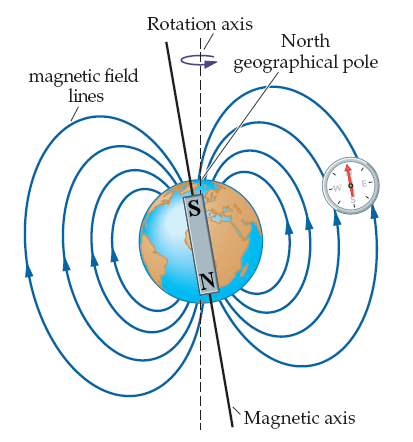
Which pole of the Earth's magnetic field is under northern Canada?
A. North
B. South
Answer
Walker5e EYU 22.1
Is pole 1 of the bar magnet a north magnetic pole (N) or a south magnetic pole (S)?
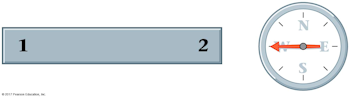
A. north (N)
B. south (S)
C. It's impossible to say
Answer
Walker5e CnEx 22-1
Can magnetic field lines cross one another?
A. yes
B. no
Answer
B. South

A. north (N)
The north pole of the compass needle is the arrow end, and it is attracted to the south pole of the bar magnet, which is marked pole 2. That means pole 1 is the north pole of the bar magnet.
B. no
A compass needle can point in only one direction at any given location. Like the electric field, the magnetic field is a vector sum of all the field contributions from nearby magnets, and the vector sum (like any other vector) can only point one direction. Two field lines that cross would suggest the magnetic field points in two directions at the same point in space.










