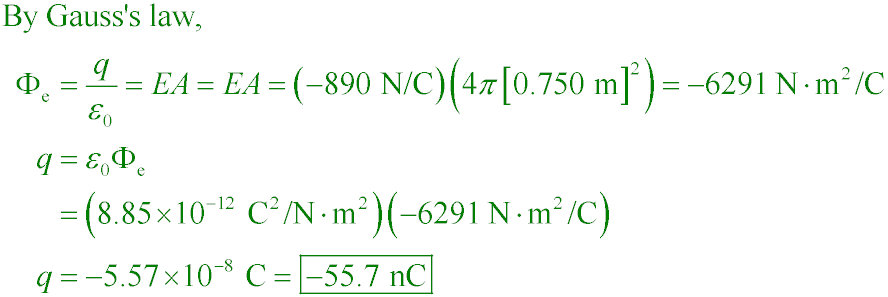Summary
- Ring of charge
- Charged particle motion
- Electric flux
- Written Quiz Chs. 21-22
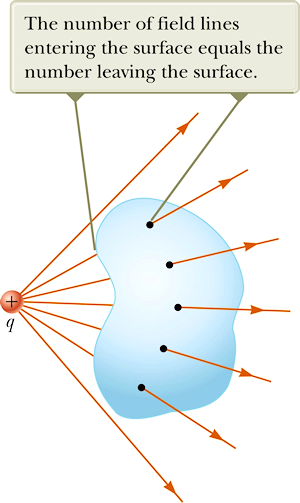
- Gauss’ law
- Prepare:
Read textbook section 23-3 through 23-6 before the next lecture
Knight2 28.stt.2
The red arrows represent the average electric field over each face of a cubical box.
We can conclude the box contains __________.
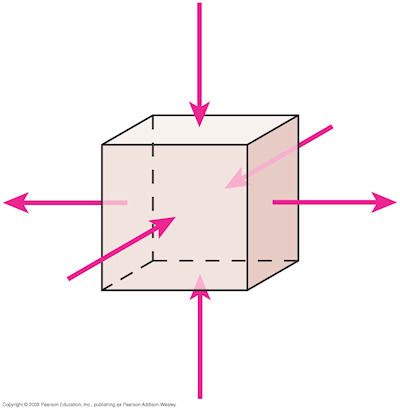
A. two positive charges
B. four negative charges
C. no net charge
D. a net positive charge
E. a net negative charge
Answer
POP4 19.32
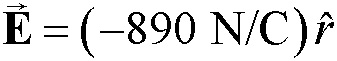 everywhere on the surface of an r = 0.750 m spherical shell. What is the net
charge inside the shell?
everywhere on the surface of an r = 0.750 m spherical shell. What is the net
charge inside the shell?
A. −41.7 nC
B. +41.7 nC
C. −55.7 nC
D. +55.7 nC
Answer
POP4 19.32
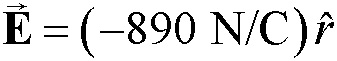 everywhere on the surface of an r = 0.750 m spherical shell.
What is the charge distribution inside?
everywhere on the surface of an r = 0.750 m spherical shell.
What is the charge distribution inside?
A. It's impossible to say.
B. It must be spherically symmetric.
C. It must be uniform throughout.
D. It must be zero at the center.
Answer
E. a net negative charge
The fact that field arrows point both inside and outside the box
implies that both kinds of charge exist in the box. Because there are more arrows pointing inward
than outward, we conclude there is a net negative charge inside the box.
C. −55.7 nC
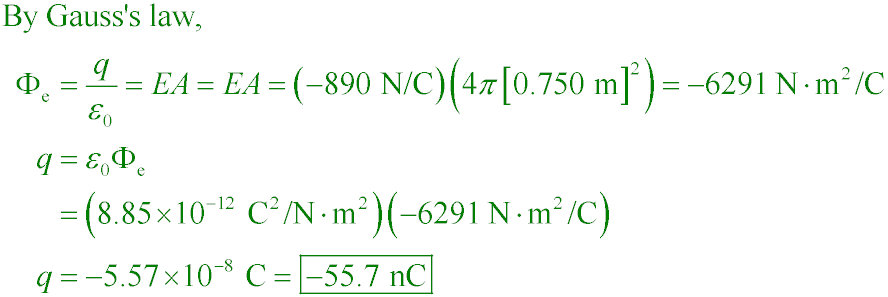
B. It must be spherically symmetric.
The fact that the field is the same everywhere on the surface
of the sphere demands that the charge be arranged in a spherically symmetric fashion. Otherwise you
would expect a greater field on one side of the surface than the other. The total flux through the
surface equals q/ε0, no matter how the charge is distributed inside, so
knowing only the total flux gives information about the total charge but not its distribution.