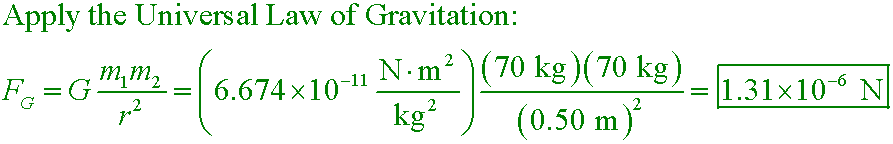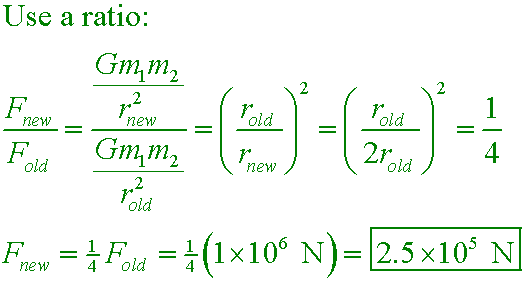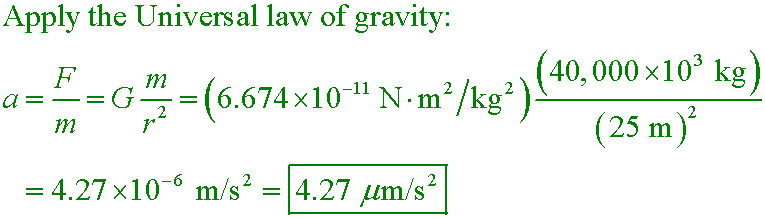Summary
- Rolling motion
- Torque & vector cross product
- Angular momentum
Chapter 12
- Static Equilibrium [also discussed in lab]
- Stability & balance
- stable equilibrium
- unstable equilibrium
- neutral equilibrium
Example #3
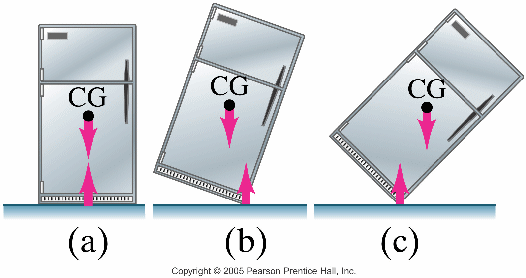
Chapter 13
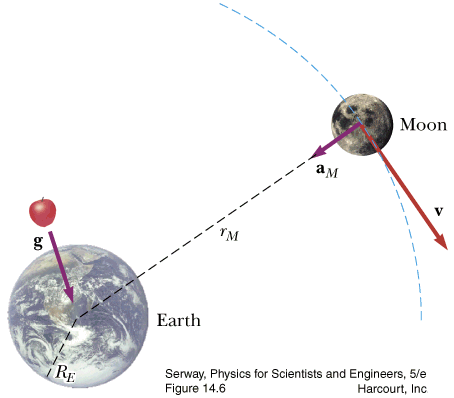

- Newton's Universal Law of Gravitation
pse6 12.24
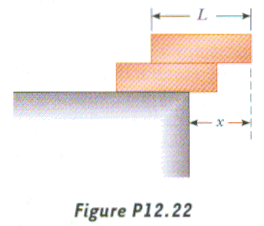
Two identical, uniform bricks of length L are stacked as shown. What is the maximum x
possible before the bricks topple and fall?
A. L
B. 3L/4
C. L/2
D. L/3
Answer
Walker5e Ex 11-11
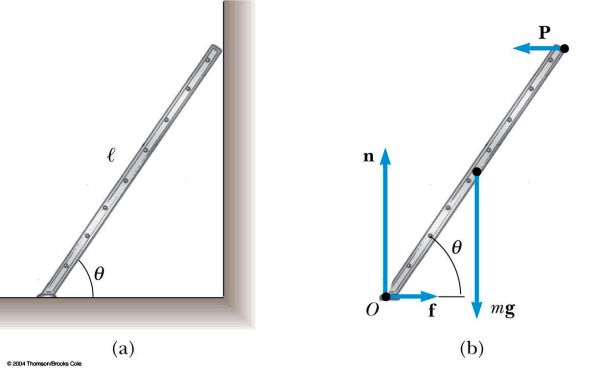
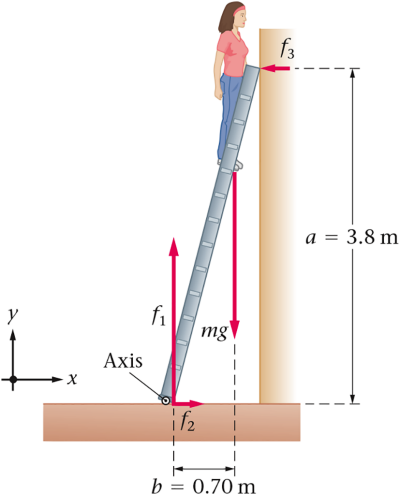
An 85-kg person stands on a lightweight ladder, as shown in the figure. The floor is rough; hence, it exerts both a normal force f1 and a frictional force f2 on the ladder. The wall is frictionless and exerts only normal force f3. Use the dimensions in the figure to find the magnitude of force f2.
 A. 85 N
A. 85 N
B. 153 N
C. 680 N
D. 833 N
Answer
gc6 9.36
The Leaning Tower of Pisa is 55 m tall and about 7.0 m in diameter. The top is 4.5 m off center.
How much farther can it lean before it becomes unstable?
 A. 1.0 m
A. 1.0 m
B. 2.5 m
C. 3.5 m
D. 4.5 m
Answer
Walker4e
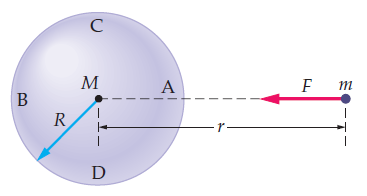
Which portion of the sphere of mass M exerts the greatest force on
the small mass m?
A. portion A
B. either portion D or C
C. portion B
D. All portions exert the same force on m.
Answer
klm
Suppose you and the person next to you are each 70 kg and are sitting 0.50 m apart. What is the force of
attraction between you and they?
A. 9.34×10−9 N
B. 1.87×10−8 N
C. 6.54×10−7 N
D. 1.31×10−6 N
Answer
klm
Two spacecraft in outer space attract each other with a force of 1×106 N. What would the attractive force be if they were twice as far apart?
A. 4.0×106 N
B. 2.0×106 N
C. 5.0×105 N
D. 2.5×105 N
Answer
PoP5 11.1mod
What is the horizontal gravitational acceleration experienced by adjacent 40,000 metric ton ships that are
25 m apart?
A. 0.00427 m/s2
B. 4.27 µm/s2
C. 427 nm/s2
D. 0.427 pm/s2
Answer
pop4 11.8
What is gEarth at the point where gEarth = gMoon? The
centers of the Earth and Moon are 384,400 km apart, and the masses are MEarth = 5.97×1024 kg and MMoon = 7.35×1022 kg.
A. 2.72 mm/s2
B. 3.33 mm/s2
C. 115 mm/s2
D. 3.46 m/s2
Answer
answer

B. 3L/4
The center of mass of the top brick must be above the point of
support, and the center of mass of the two-brick combination must also be above its point of
support. The solution becomes more interesting as you consider more bricks:



If you're interested, read more about how
alternative strategies can lead to a maximum overhang of
N1/3
answer

B. 153 N
Set the torques about the bottom of the ladder (marked "Axis") equal to zero. Examine the diagram to see the torque due to the person's weight is −mgb (clockwise, so negative), and the torque due to f3 is +a f3. You will find f3 is 153 N, then set the sum of the horizontal forces equal to zero to find f2 = f3.
answer
B. 2.5 m
The top would have to move one diameter in order to put the center gravity, assumed to be halfway
down, over the pivot point of one side of the base. It can therefore move 7.0 m − 4.5 m = 2.5 m further.
answer

A. portion A
The force increases when the distance r decreases, so the
nearest portion of the mass M exerts the greatest force on m. The combined force from
all portions acts as if all of the mass M were concentrated at its center.
answer
D. 1.31×10−6 N
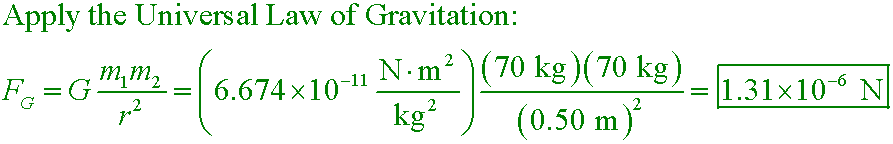
answer
D. 2.5×105 N
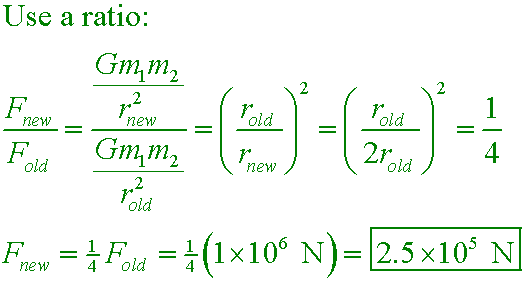
answer
B. 4.27 µm/s2
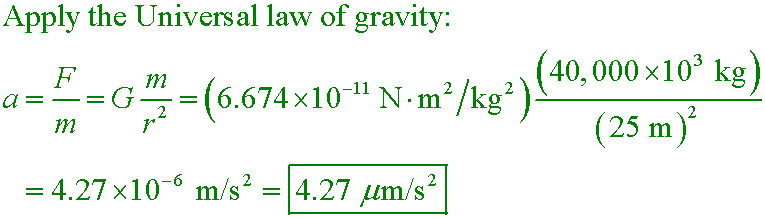
answer
B. 3.33 mm/s2









 A. 85 N
A. 85 N A. 1.0 m
A. 1.0 m