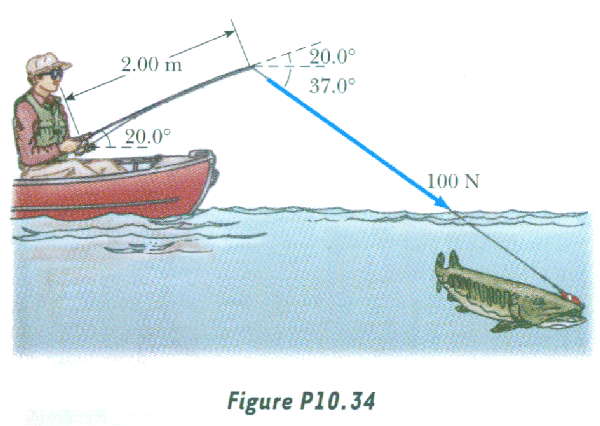
Bonus question Ch.09


- rotational kinetic energy Example #1
Example #2
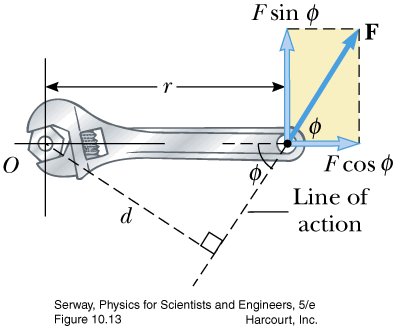
- definition, units
- torque vectors applet Example #3
I have not yet found HTML5 equivalents to these torque applets. Sorry!



I have not yet found HTML5 equivalents to these torque applets. Sorry!