Today's joke

- definition
- apple on tree
- fan cart and sail video Example #1
- contact forces interactive applet
- airplanes and rockets
Example #2
Example #3
I have not yet found an HTML5 equivalent to this applet. Sorry!
Example #4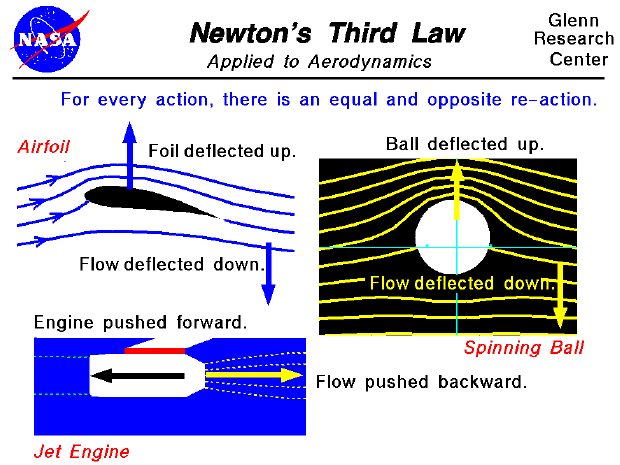

I have not yet found an HTML5 equivalent to this applet. Sorry!
Example #4
 A. Gravity provides added force
A. Gravity provides added force A. zero
A. zero A. greater than
A. greater than

