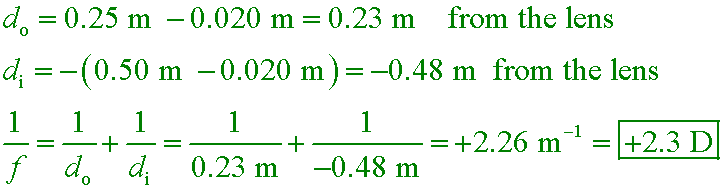Summary
- Total internal reflection
- Thin lenses
- Dispersion & rainbows
- Today's joke
Chapter 27
- The human eye
- optical arrangement
- nearsighted
Example #1
Example #2
- farsighted
- astigmatic
- refractive power (diopters)
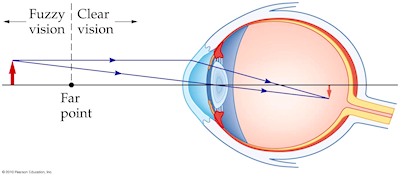
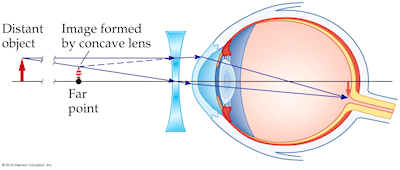
| The Nearsighted Eye |
|---|
| uncorrected | corrected |
|---|
 |
 |
|
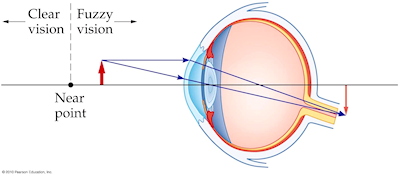
| The Farsighted Eye |
|---|
| uncorrected | corrected |
|---|
 |
 |
- Lecture learning outcomes
A student who masters the topics in this lecture will be able to:
- describe the defects of nearsighted and farsighted eyes, and explain qualitatively how vision can be corrected for each
- calculate the focal length of eyeglasses (or contact lenses) that will correct either nearsighted or farsighted vision
- draw a ray diagram that illustrates qualitatively how nearsighted or farsighted vision can be corrected (students do not need to draw exact ray diagrams for systems with more than one optical element)
- use the lens equation to calculate the refractive power of a corrective lens
Practice:
Try these additional examples
Example #3
Example #4
Example #5
Prepare:
Read textbook section 27-3 before the next lecture
sj6 36.q19
 Is this person nearsighted or farsighted?
Is this person nearsighted or farsighted?
A. nearsighted
B. farsighted
C. neither
D. impossible to say
Answer
gc6 25.13
A person has a far point of 14 cm. What power contact lenses would the person need?
A. +7.14 D
B. +4.00 D
C. −7.14 D
D. −14.3 D
Answer
Walker5e 27.EYU.2 question A
When a nearsighted eye focuses on an object at infinity, does it form an image that is in front of the retina, on the retina, or behind the retina?
A. in front of the retina
B. on the retina
C. behind the retina
D. It depends upon how severe is the person's nearsightedness.
Answer
Walker5e 27.43bc
With unaided vision, a librarian can focus only on objects that lie at distances between 5.0 m and 0.50 m. Find the refractive power that will correct his farsightedness.
A. −0.20 D
B. −4.8 D
C. +0.23 D
D. +2.3 D
Answer
klm
Reading glasses produce an upright, magnified image of a nearby book to a location farther from the person's eyes. Therefore, reading glasses can also correct
A. nearsightedness
B. farsightedness
C. astigmatism
D. none of above
Answer
A. nearsighted
The upright, reduced, virtual image of the man's face behind the lens indicates the lens is
diverging. Diverging lenses are used to correct nearsightedness. The converging lens for a farsighted person would produce an upright,
magnified, virtual image of the face. Here is a comparison, nearsighted on the left and farsighted
on the right:


C. −7.14 D

A. in front of the retina
The nearsighted eye is slightly elongated, and it forms the image of a distant object in front of the retina. A diverging corrective lens expands the rays a little bit so the image forms farther from the lens and directly on the retina.
| The Nearsighted Eye |
|---|
| uncorrected | corrected |
|---|
 |
 |
D. +2.3 D
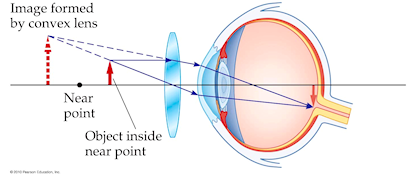
The librarian is nearsighted because his far point is 5.0 m instead of infinity. He is also farsighted because his near point is 0.50 m instead of 0.25 m. To correct his farsighted vision, a converging lens is needed to put the upright, magnified image of an object 0.25 m from his eye (standard reading distance) at 0.50 m from his eye, where he can see it clearly. Notice that the object and image distances for the prescription refer to distance from the lens, not from his eye, so there is a 2.0-cm adjustment to the distances.
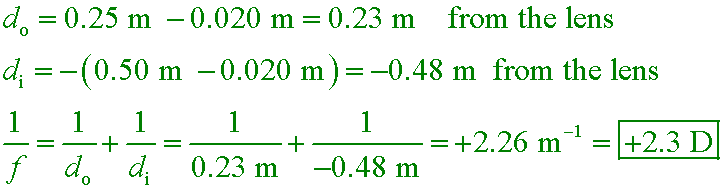
B. farsightedness
Only converging lenses can produce an upright, magnified image at a greater
distance than the object distance. (This occurs when the object is less than one focal length from the lens.)
Because farsightedness can be corrected with converging lenses, reading glasses can be useful for this purpose.




 Is this person nearsighted or farsighted?
Is this person nearsighted or farsighted?