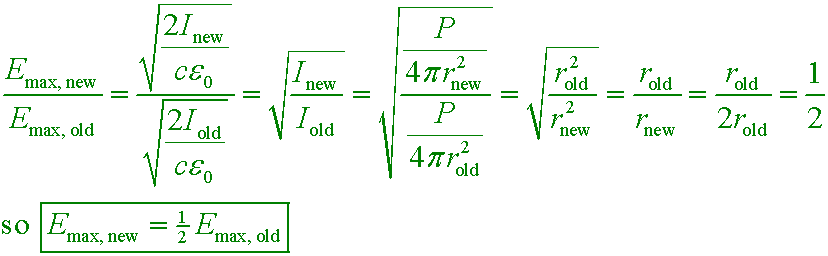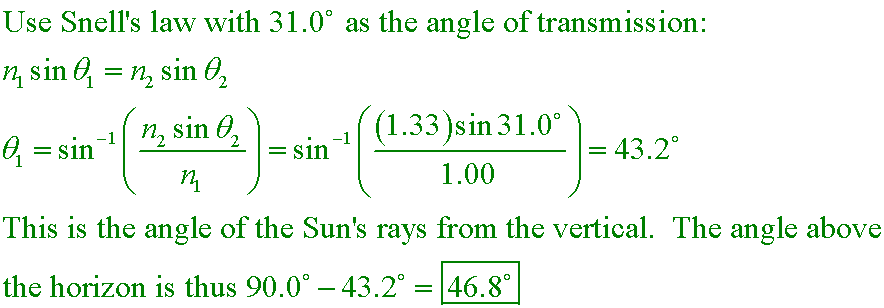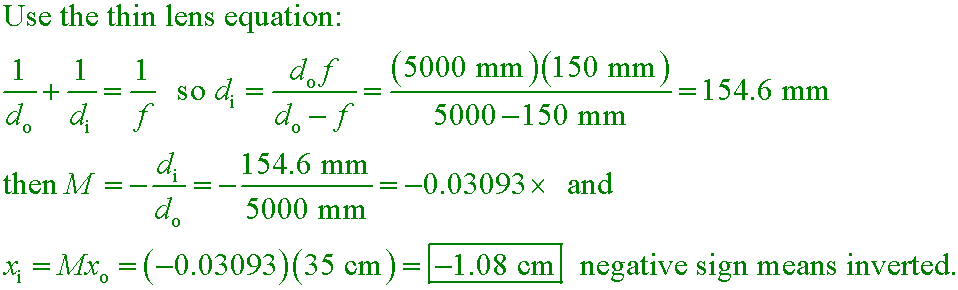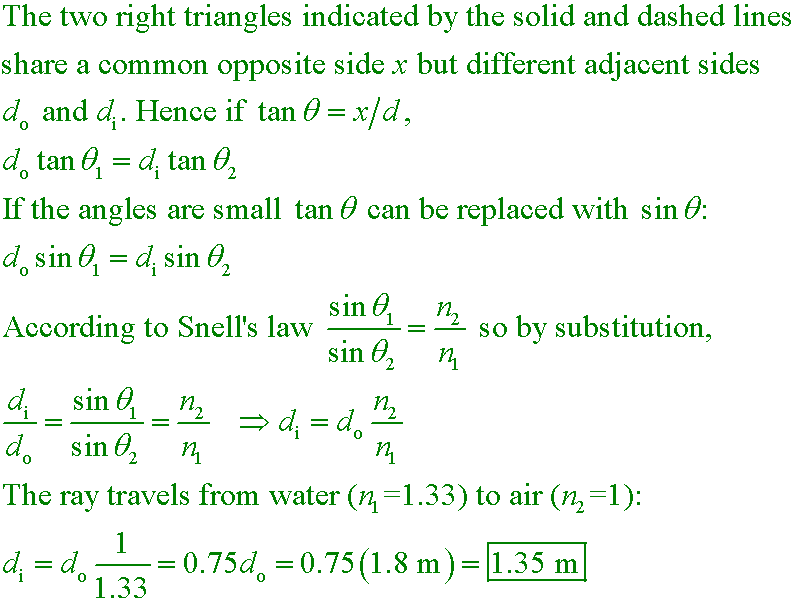 Summary
Summary
- Light rays
- Law of reflection
- Plane and spherical mirrors
- Quiz Bonus Ch. 25


- Refraction



- Thin lenses and curved mirror PhET applet
- Thin lenses simple applet
- three principal rays
- thin lens equation
- sign convention
- magnification
Example #3
- Lecture learning outcomes
A student who masters the topics in this lecture will be able to:
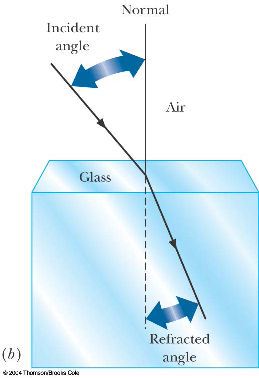
- describe the refraction of light in terms of changes in the direction of wave propagation and of wavelength
- predict the location of a virtual image created by refraction at a plane surface
- use algebra to find the index of refraction n (of medium 1 or medium 2) or angle θ (in medium 1 or medium 2) for a refracted ray when any three of these quantities are given
- be able to describe and calculate the critical angle for total internal reflection
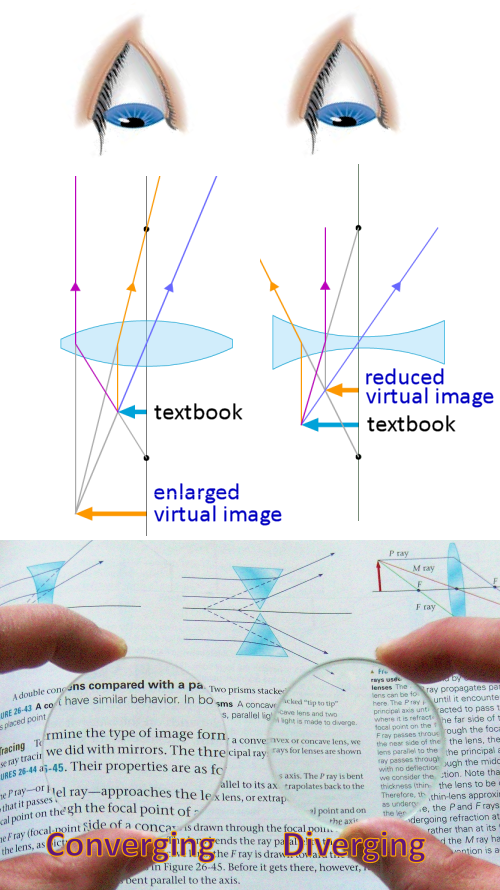
- draw a ray diagram with three principal rays to predict the image location, orientation, and size for either a converging or a diverging lens
- use algebra to find the object distance do, image distance di, or focal length f for a thin lens when any two of these quantities are given
Practice:
Try these additional examples
Example #4
Example #5
Example #6
Prepare:
Read textbook section 26-8 before the next lecture
Walker5e Ex.25-8 practice
The amplitude of the electric field a distance of 1.00 m from a 50-W light bulb is Emax. At a
distance of 2.00 m from the light bulb, Emax _____.
A. increases by a factor of √2
B. decreases by a factor of √2
C. decreases by a factor of 2
D. decreases by a factor of 4
Answer
klm
A light ray exits glass (n = 1.50) and enters water (n = 1.33). Which way does the ray go?
A. It bends toward the normal.
B. It bends away from the normal.
C. It does not bend.
D. It totally reflects off the interface.
Answer
gc6 23.29
Rays of the Sun are seen to make a 31.0° angle to the vertical by an underwater observer.
At what angle above the horizon is the Sun?
A. 31.0°
B. 59.0°
C. 43.2°
D. 46.8°
Answer
klm
A 35-cm-long squirrel is photographed with a l50 mm focal length lens when it is 5.0 meters from the camera. What is the
size of the squirrel's image on the film?
A. 1.08 cm
B. 1.17 cm
C. 8.57 mm
D. 2.33 mm
Answer
Walker5e 26.55
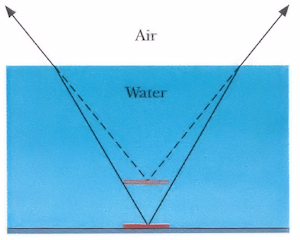
A coin is lying at the bottom of a pool of water that is 1.8 m deep. When viewed from directly above, how far below the surface of the water does the coin appear to be?
A. 0.45 m
B. 1.35 m
C. 1.80 m
D. 2.40 m
Answer
Walker5e CnEx 26-17
If a converging lens is immersed in water instead of air, does its focal length increase, decrease, or stay the same?
A. increase
B. decrease
C. stay the same
Answer
Walker5e EYU 26.6
The lenses shown below have objects that are identical in size and location relative to the lens. Is the image produced by lens 1 larger than, smaller than, or the same size as the image formed by lens 2?
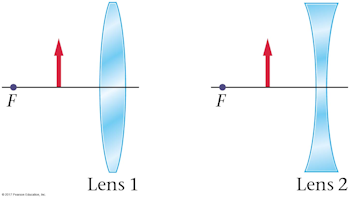
A. larger than
B. smaller than
C. the same size as
Answer
C. decreases by a factor of 2
The intensity decreases by a factor of 4 because the distance to the point source of light is doubled. The amplitude Emax is proportional to the square root of the intensity, so
it decreases by a factor of 2.
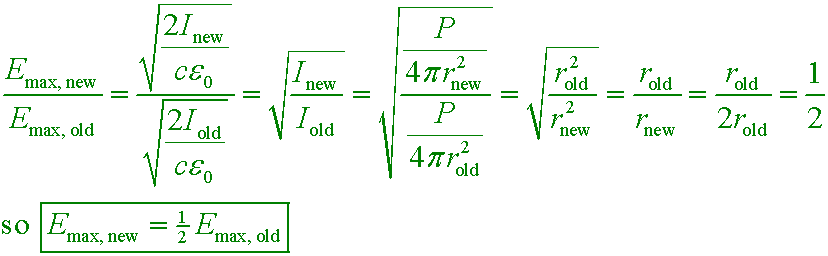
B. It bends away from the normal.
The wave must speed up as it enters a medium with a lower index of refraction.
It must therefore bend away from the normal.
D. 46.8°
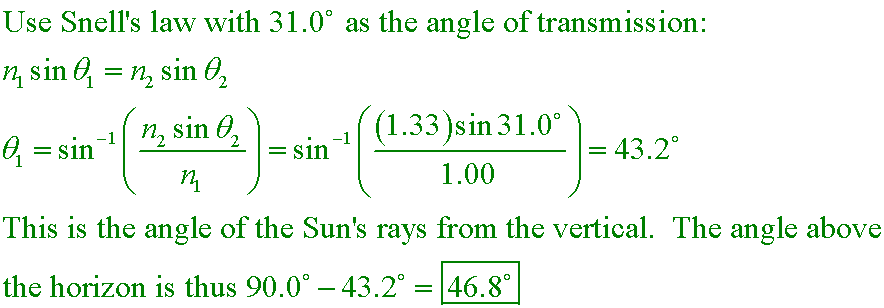
A. 1.08 cm
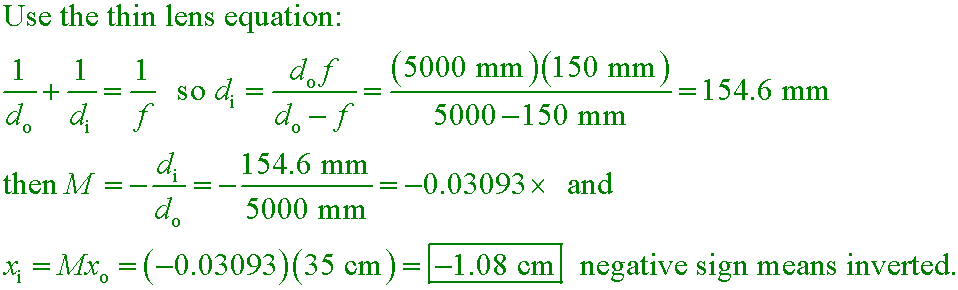
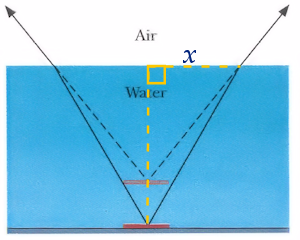
B. 1.35 m
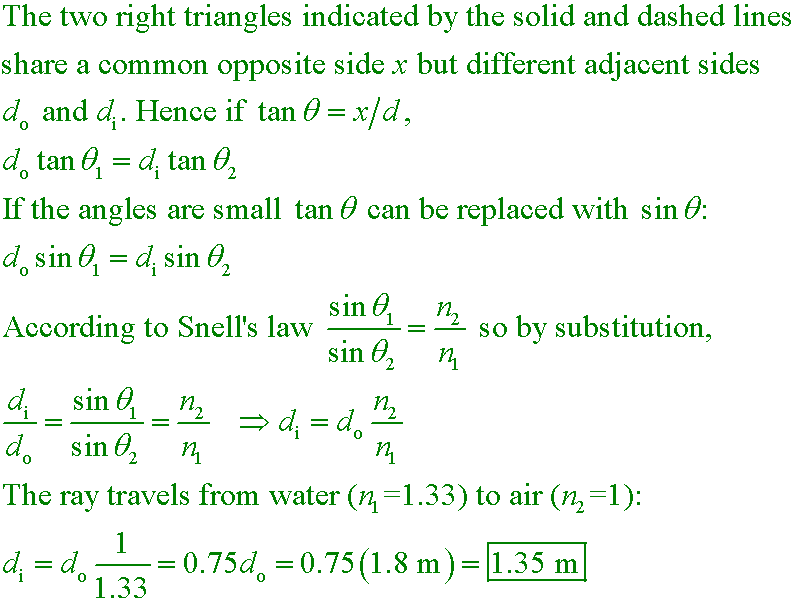
Refraction makes the image of the coin appear shallower than it is by a factor of nair/nwater = 1/1.33 = 3/4.
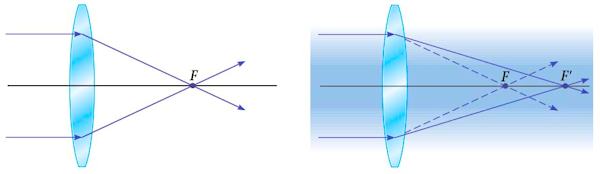
A. increase
There is a smaller difference of index of refraction between water and glass than between air and glass. As a result, the light rays bend less at each boundary and the focal length of the lens becomes longer.

A. larger than
The image produced by lens 1 will be virtual, upright, and magnified. The image produced by lens 2 will be virtual, upright, and reduced.






 Summary
Summary