Summary
- Faraday's law
- Lenz's law
- Transformers
- Written Quiz Ch. 22
Chapter 25
- Electromagnetic radiation
- Lecture learning outcomes
A student who masters the topics in this lecture will be able to:
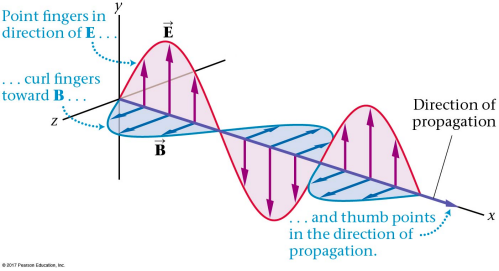
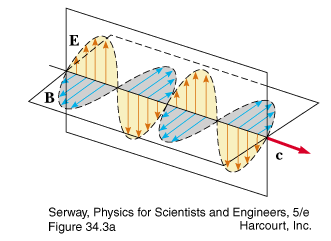
- describe the basic features of an electromagnetic wave, including the speed of propagation and the relative orientations of the electric and magnetic fields
Practice:
Try these additional examples
Example #1
Example #2
Prepare:
Read textbook sections 25-2 through 25-4 before the next lecture
Walker5e 25.01
If the electric field in an electromagnetic wave is increasing in magnitude at a particular time, the magnitude of the magnetic field at the same time is _____.
A. increasing
B. decreasing
C. staying the same
Answer
Walker5e 25.02
The electric field of an electromagnetic wave points in the positive y direction. At the same time, the magnetic field of this wave points in the positive z direction. In what direction is the wave traveling?
A. negative x direction
B. negative y direction
C. negative z direction
D. positive x direction
Answer
A. increasing
The electric and magnetic fields are correlated to each other; when one increases, so does the other. Refer either to Figure 25-4 or to Equation 25-9, E = cB.

D. positive x direction
Point the fingers of your right hand in the direction of E (positive y direction) and curl your fingers toward B (positive z direction), and your thumb points in the direction of propagation (positive x direction).


