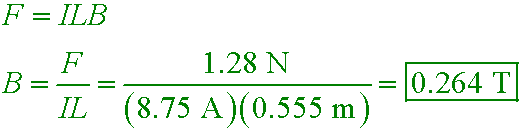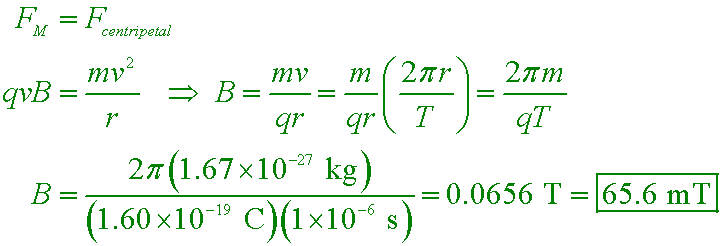Summary
- Magnets
- Magnetic fields
- Currents produce magnetic fields

About the photo
Lecture learning outcomes
A student who masters the topics in this lecture will be able to:
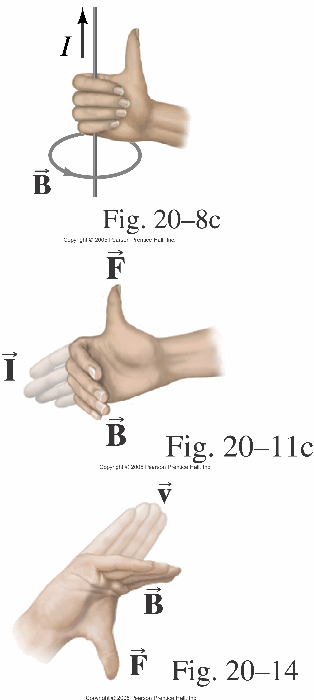
- use the appropriate right-hand rule to predict the direction of the magnetic force exerted on a charged particle that moves in a region of magnetic field
- use algebra to find the magnetic force F, current I, length L, magnetic field B, or angle θ when any four of these quantities are given
- use algebra to find the magnetic force F, charge q, velocity v, magnetic field B, or angle θ when any four of these quantities are given
- explain the helical motion of a charged particle that moves in a uniform magnetic field
Practice:
Try these additional examples
Example #3
Example #4
Prepare:
Read textbook sections 22-6 and 22-7 before the next lecture
gc6 20.5
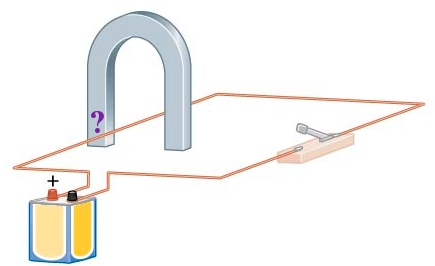
The force on a wire carrying 8.75 A is a maximum of 1.28 N when placed between the pole faces
of a magnet that are 55.5 cm in diameter. What is the approximate strength of the magnetic field?
A. 1.28 T
B. 0.875 T
C. 0.379 T
D. 0.264 T
Answer
sj6 29.34
A proton moving in a circular path has a period of 1.00 µs. What is B?
A. 1.00 µT
B. 55.2 µT
C. 33.3 mT
D. 65.6 mT
Answer
sj6 29.8
If B = 50 µT northward and E=100 N/C downward, how do the force magnitudes on an
electron with velocity 6000 km/s eastward compare?
A. gravity > electric > magnetic
B. electric > gravity > magnetic
C. magnetic > electric > gravity
D. electric > magnetic > gravity
Answer
Walker5e CnEx 22-12
When the switch is closed the wire between the poles of the horseshoe magnet deflects downward. Is the left end of the magnet a north magnetic pole or a south magnetic pole?
A. north
B. south
C. either pole produces a downward deflection
Answer
D. 0.264 T
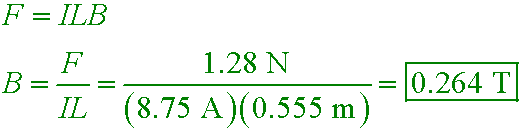
D. 65.6 mT
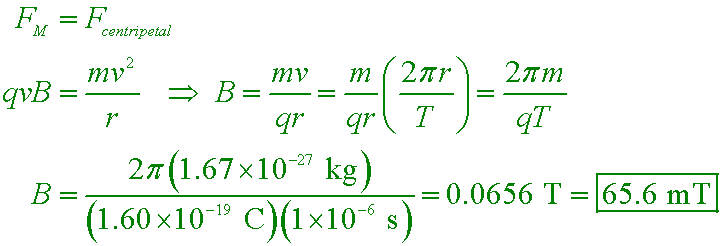
C. magnetic > electric > gravity
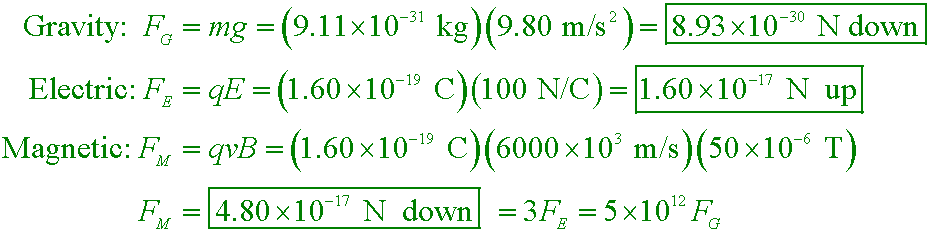

A. north
Using the right-hand-rule, if your thumb points downward (the direction of the force) your fingers curl toward the right (the direction of the magnetic field). Magnetic fields come out of the north pole and enter the south pole of a magnet.