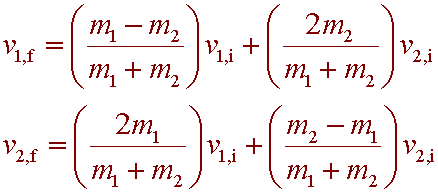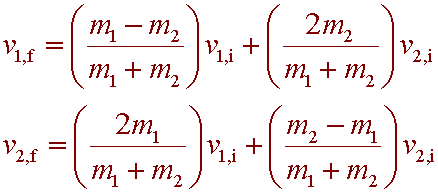Summary
- Friction & nonconservative work
- Momentum
- Conservation of momentum
walker4
Reading quiz A person pushes with 50 N of force to separate two canoes that are initially at rest.
If the person pushes for 1.20 s, find the magnitude of the momenta of each canoe after the push.

A. 24 kg·m/s
B. 60 kg·m/s
C. 41.7 kg·m/s
D. The masses are required to answer this question.
Answer
sj6 9.18
A 25,000 kg railcar moving at 4.0 m/s collides and couples together with three identical cars moving
in the same direction at 2.0 m/s. What energy is lost in the collision?
A. zero
B. 313 kJ
C. 50 kJ
D. 37.5 kJ
Answer
gc6 7.25
An m = 0.060 kg ball, moving at +2.50 m/s, collides head-on with an M = 0.090 kg ball initially moving away from it at a speed of +1.15 m/s.
Assuming a perfectly elastic collision, what are the velocities of each ball after the collision (m, M)?
A. −0.44 m/s, +4.46 m/s
B. 0, +3.65 m/s
C. +0.88 m/s, +2.23 m/s
D. −1.35 m/s, +1.35 m/s
Answer
gc6 ex7-4
A 5.0 kg rifle fires a 0.020 kg bullet at 620 m/s. What is the recoil speed of the rifle?
A. 2.5 m/s
B. 0.40 m/s
C. 0.080 m/s
D. 12.4 m/s
Answer
B. 60 kg·m/s
The change of momentum of each canoe equals the impulse that is
delivered. The impulse is the product of the force and the time interval, so
(50 N)(1.20 s) = 60 kg·m/s
D. 37.5 kJ

C. +0.88 m/s, +2.23 m/s

A. 2.5 m/s